Overview of Wrist (Distal Radius) Fractures
Before we start, lets help clear up some terms.
By definition, any break in any bone is called a fracture.
Broken Wrist- non-specific term that means that one of the bones around the wrist joint is broken
Fractured Wrist- non-specific term that means one of the bones about the wrist joint is broken
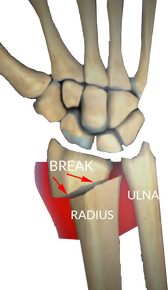
Distal Radius Fracture- when the radius, the larger bone in the forearm, is broken by the wrist joint
Displaced fracture- the bone is not in satisfactory alignment and will not heal well if left as is
Non-displaced fracture- the bone is in good alignment and will likely heal as is, without surgical intervention
Some terms you may hear for these types of breaks are Colles fracture, Barton's fracture, radial styloid fracture, Smith fracture. All of these terms are specific patterns in which the wrist breaks
By definition, any break in any bone is called a fracture.
Broken Wrist- non-specific term that means that one of the bones around the wrist joint is broken
Fractured Wrist- non-specific term that means one of the bones about the wrist joint is broken
Distal Radius Fracture- when the radius, the larger bone in the forearm, is broken by the wrist joint
Displaced fracture- the bone is not in satisfactory alignment and will not heal well if left as is
Non-displaced fracture- the bone is in good alignment and will likely heal as is, without surgical intervention
Some terms you may hear for these types of breaks are Colles fracture, Barton's fracture, radial styloid fracture, Smith fracture. All of these terms are specific patterns in which the wrist breaks
Causes
|
Most distal radius fractures, also known as wrist fractures, are caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. As you extend your wrist to prevent your fall, when you land a large force is placed on the wrist causing it to break. Most wrist fractures occur with a slip and fall while trying to protect themselves.
|
Who gets wrist fractures?
|
Most wrist fractures occur in patients older than 50. Wrist fractures are delineated into low impact and high impact. Older patients tend to have softer and weaker bone (osteoporosis and osteomalacia) compared to younger patients and therefore are more likely to sustain low impact breaks. In order to break the bone of a younger person, usually a much higher force is required to lead to a break.
Some terms you may hear for these types of breaks are Colles fracture, Barton's fracture, radial styloid fracture, Smith fracture. All of these terms are specific patterns in which the wrist breaks |
Conservative (Non-Operative) Treatment
|
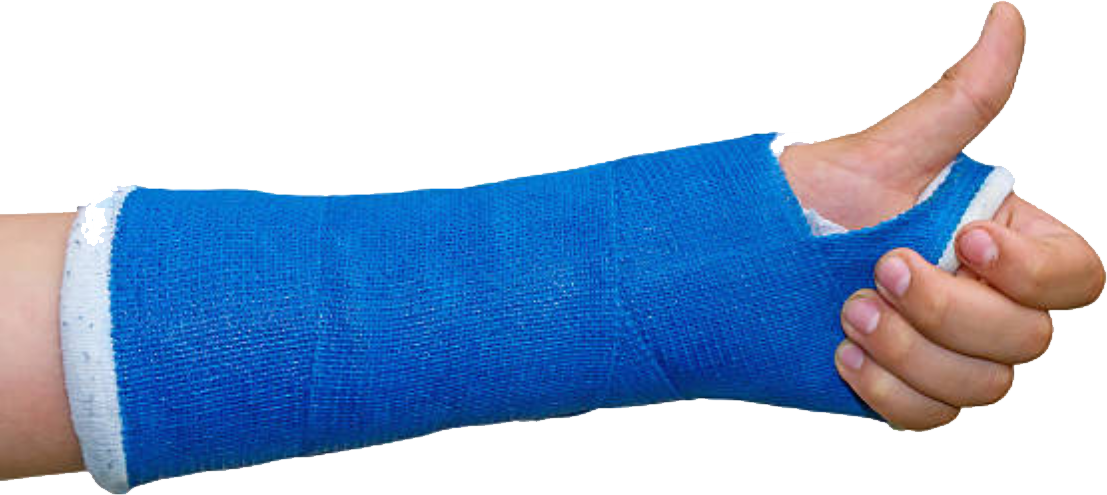
Most fractures can be treated conservatively with just a cast. Most conservative (non-operative) treatment will consist of a cast and/or wrist brace for 4-6 weeks, depending on the break. With more severe breaks, a closed reduction will be attempted. A closed reduction is where one of our doctors will apply traction and pressure to the break to put it back into normal alignment. Once adequate alignment is obtained, a cast will be applied to hold the bone into its restored position.
|
Surgical Treatment
|
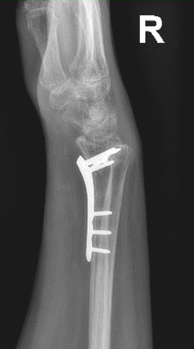
If the break is too severe and displaced (out of normal position), a surgery may be recommended as part of your treatment. Surgeries are very succesful and allow earlier and more predictable range of motion early after surgery. Most commonly, a plate and screws is placed into the broken bone once the normal alignment is obtained during the surgical procedure.
|
Rehabilitation of a Broken Wrist
|
After conservative management or surgical managment, a short course of physical therapy is usually recommended. In physical therapy, excercises to regain motion and grip strength may be used to help you get your hand function back as quickly as possible. We tell all patients that the wrist may swell and be painful for up to 6-12 months after the initial break.
|
Office HoursMon-Fri: 9AM-5PM
|
Telephone |
High School Football Season Added Coverage HoursSaturdays During High School Football Season
Injury Clinic is for INJURED PLAYERS ONLY. Snellville ONLY. 9AM-10AM MEDIA ROOM |